|
|
|
|
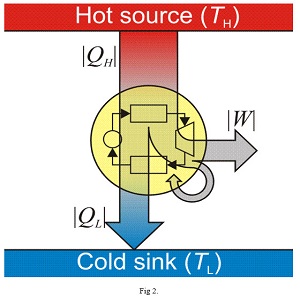
CA2,958,456
2019/02/21 A method and apparatus for load balancing trapped solar energy using
smallmasses of low-boiling-point fluids to absorb heat in an evaporator situated in
higher heat reservoir near the ocean surface using the latent heat of evaporation to convert a portion
of the heat to another form of energy in a turbine or other heat engine,
providing a variety of energy related service applications to end users from the converted
energy, depositing a residuallatent heat of evaporation in a deep ocean heat exchanger situated in the
lower heat reservoir, using the cold seawater as a heat sink.
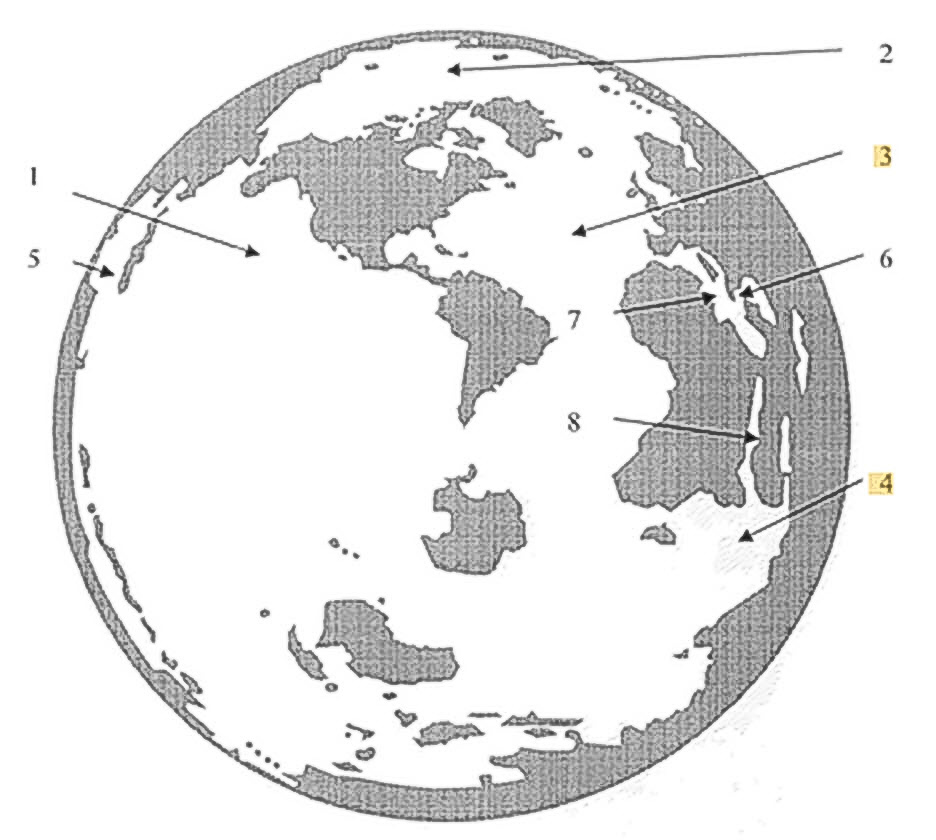
US20100251789A1 Global Warming Mitigation Method, The present invention provides
a method of sequestering carbon dioxide and water in a desert environment. In a
first step heat that would otherwise cause thermal expansion of the ocean and
resultant sea level rise is extracted to produce energy. A portion of the energy
is used to desalinate seawater. The desalinate water is pumped into a desert
environment and vegetation is planted in the irrigated desert portion. The
vegetation sequesters carbon dioxide. The seawater extracted for desalination
further reduces sea level rise. Irrigation water moderates the day and nighttime
temperature fluctuations of hot deserts. Lowering the daytime temperature
increases the deserts potential to sequester water. The commercial and arable
potential of the desert is augmented by the enrichment of its soil by composted
vegetation, its irrigation and the moderation of its diurnal temperature
fluctuations.
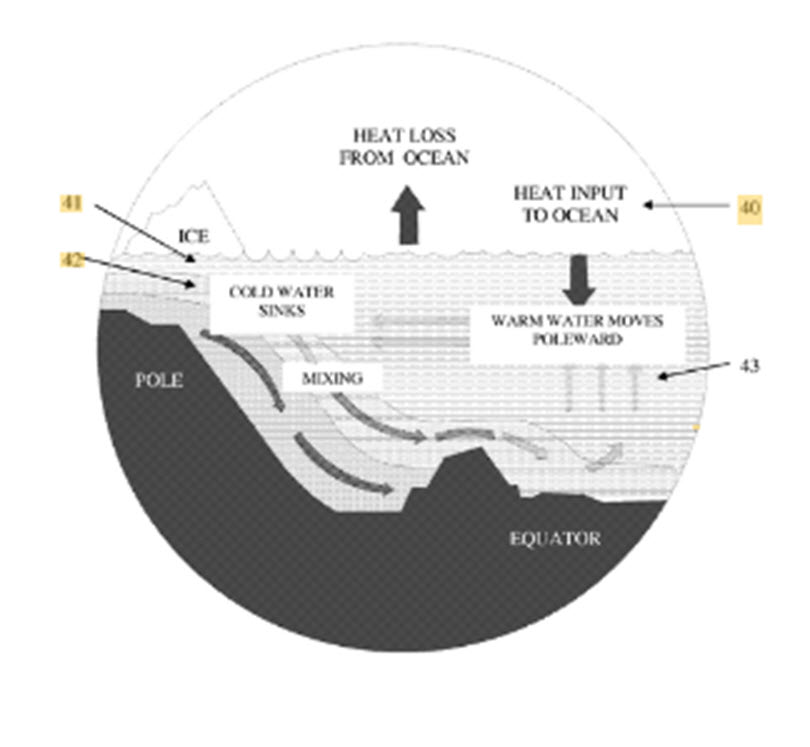
US20110036919A1 Global warming mitigation method The present invention provides
a method of limiting sea level rise. In a first step heat that would otherwise
cause thermal expansion of the ocean and resultant sea level rise is extracted
to produce energy. The energy is used to convert a portion of the liquid ocean
water to the gaseous elements hydrogen and oxygen by the process of
electrolysis. The ocean level is reduced by the volume of water converted to
gas. The hydrogen is captured for use as an energy source and is transported to
a desert to be recombined with resident oxygen to produce energy and water for
irrigation.
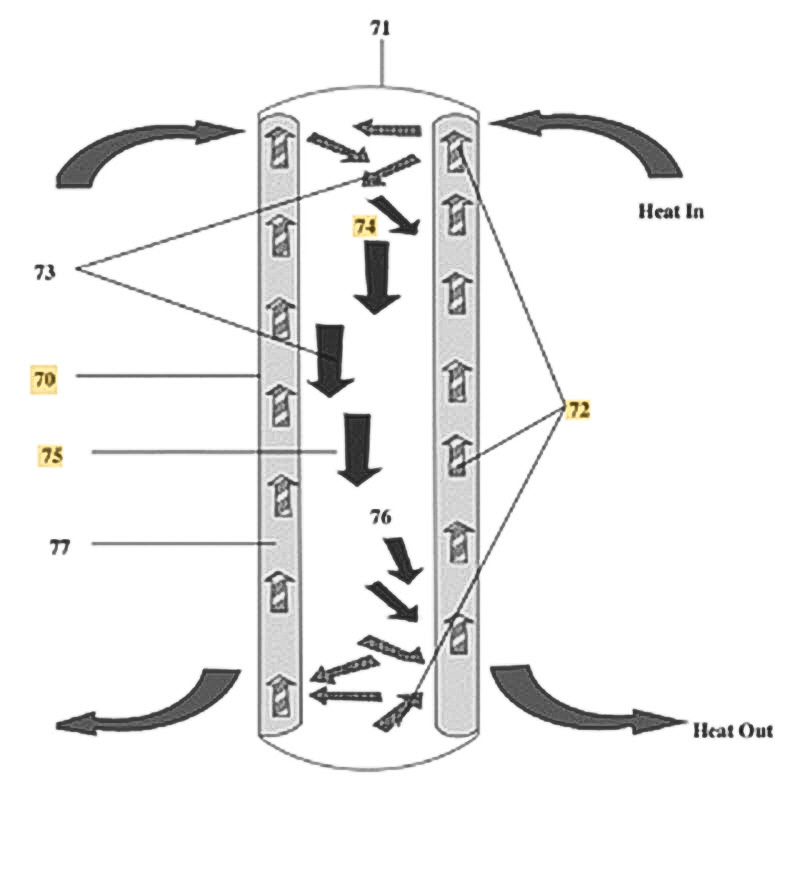
US20120234006A1 Ocean thermal energy conversion counter-current heat transfer
system,for OTEC (Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion), rather than transferring
large quantities of surface heat from near the ocean surfacUS20110036919A1
Global warming mitigation method, The present invention provides a method of
limiting sea level rise. In a first step heat that would otherwise cause thermal
expansion of the ocean and resultant sea level rise is extracted to produce
energy. The energy is used to convert a portion of the liquid ocean water to the
gaseous elements hydrogen and oxygen by the process of electrolysis. The ocean
level is reduced by the volume of water converted to gas. The hydrogen is
captured for use as an energy source and is transported to a desert to be
recombined with resident oxygen to produce energy and water for irrigation.
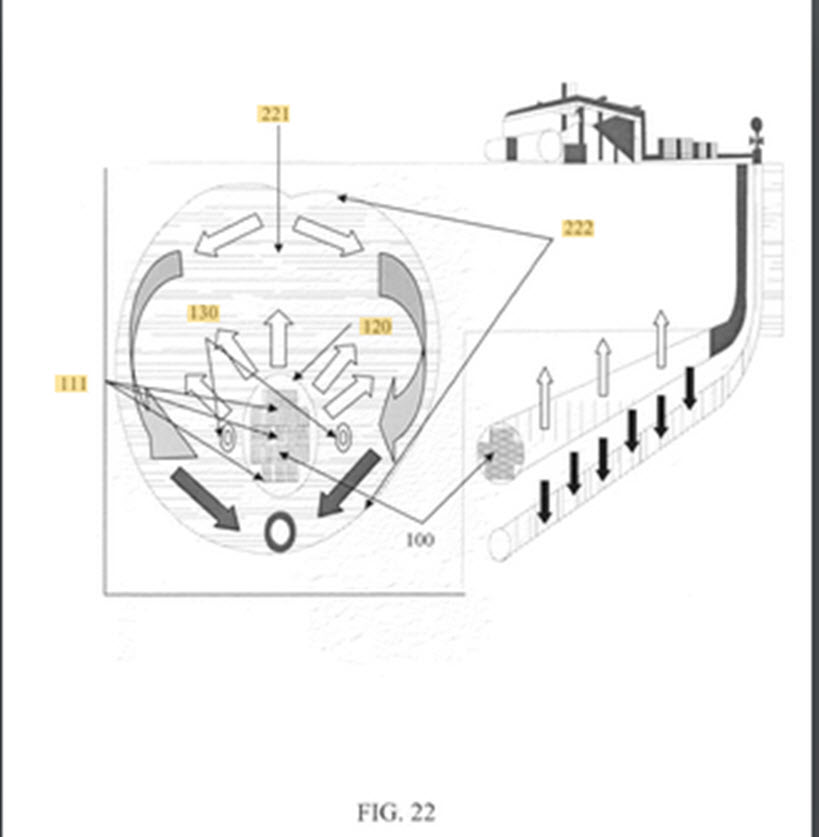
US20100105975A1 CA2659302A1 Nuclear Assisted Hydrocarbon Production Method, A
method is disclosed for the temporary or permanent storage of nuclear waste
materials comprising the placing of waste materials into one or more
repositories or boreholes constructed into an unconventional oil formation. The
thermal flux of the waste materials fracture the formation, alters the chemical
and/or physical properties of hydrocarbon material within the subterranean
formation to allow removal of the altered material. A mixture of hydrocarbons,
hydrogen, and/or other formation fluids are produced from the formation. The
radioactivity of high-level radioactive waste affords proliferation resistance
to plutonium placed in the periphery of the repository or the deepest portion of
a borehole.
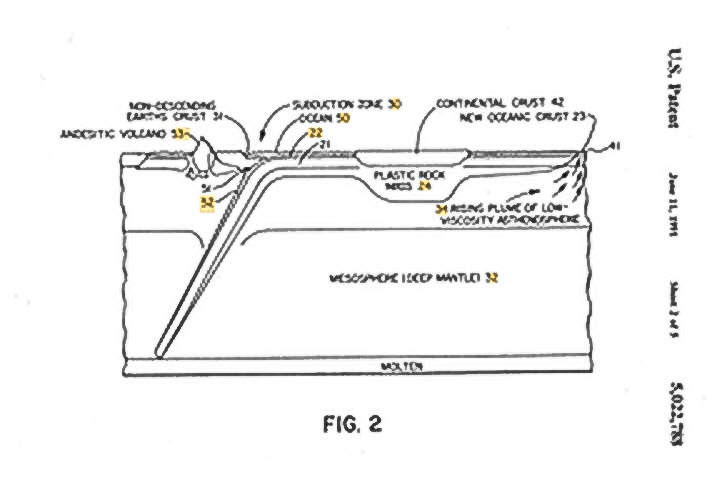
CA2005376C, US5,022,788, NZ232248, Subductive waste disposal method A method for
the disposal of nuclear and toxic waste materials comprising the placing of
waste materials into waste repositories radiating from an access tunnel
constructed into a subtending tectonic plate adjacent or as near as possible a
subduction zone. The waste materials descend within the tectonic plate into the
mantle of the earth.
The licensing of either of the last two technologies could
have provided the funding necessary to solve global warming.
Instead that problem and that of nuclear waste
remain unresolved.
|
|
|
|
CA2,958,456
US20100251789A1
US20110036919A1
US20120234006A1
US20100105975A1 CA2659302A1
CA2005376C, US5,022,788, NZ232248,
|